ANSYS and Plastic Strains
ANSYS workbench is rather unusual in how it takes inputs for stress-strain curves. Typically, the strain data in stress-strain curves represents total strain. ANSYS workbench requires that the user inputs plastic strain instead of total strain. The total strain must be converted into plastic strain before it can be used with ANSYS workbench.
The figures below shows the relationship between total, plastic and elastic strain.
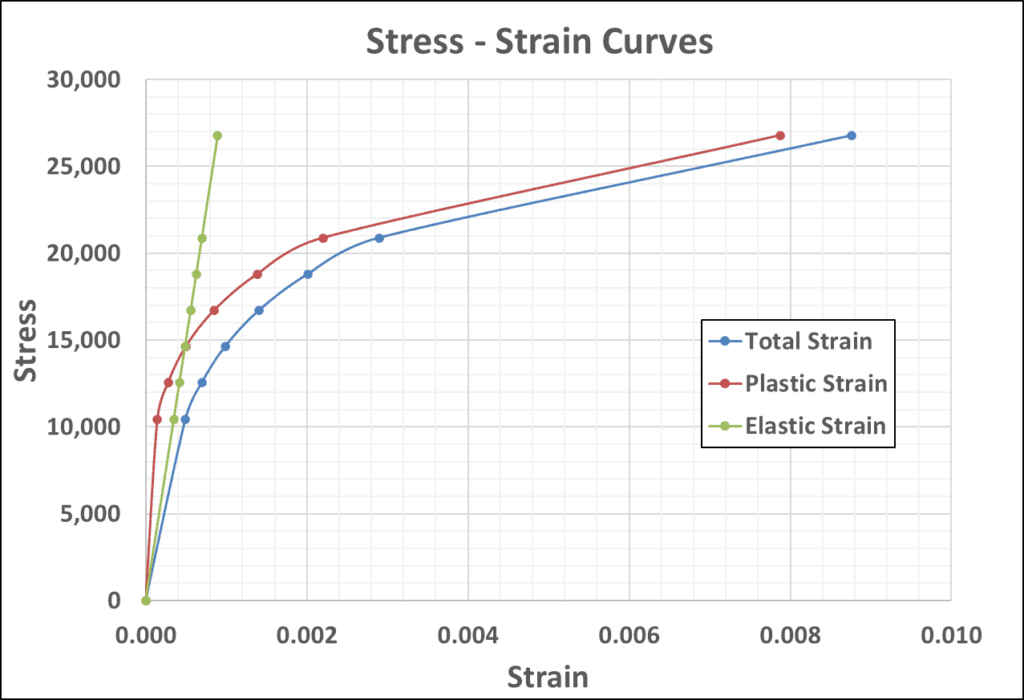
The total strain is composed of contributions from plastic and elastic strains as shown. The strain components can be calculated as follows:
ϵel = σ / E
ϵtotal = ϵp + ϵel

Converting Total Strain into Plastic Strain
How to input the data in ANSYS Workbench
Once you have the stress-strain data, you can proceed to input it in ANSYS workbench.
Step 1: Go to Engineering Data
Go to your ANSYS project and click on Engineering Data.

Step 2: Select the material for which you want to input the material curve
Under “outline of Schematic” select the material of interest. In the image below, Alloy 625 has been selected.

Step 3: Add the plasticity model of choice
You now have to select an appropriate plasticity model (See ANSYS Plasticity Models Explained for more information on the available choices). Go to the model of choice and double click. This will add the chosen model as an option under the properties of the material.

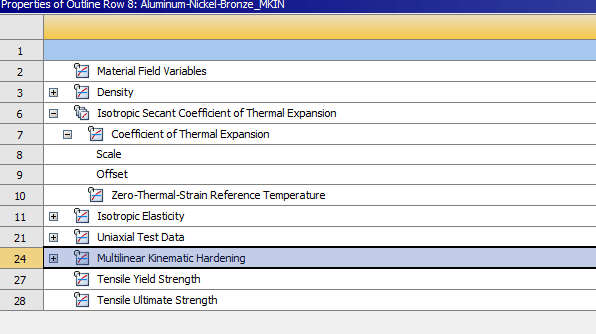
Step 4: Select the plasticity model from material properties
In the example below Multilinear Kinematic Hardening appears under the material properties
Step 5: Input the stress – strain data
The final step is to insert the stress strain data as shown below. The stress curves is valid at a selected temperature. You have to specify the temperature under Column A. You can also define multiple curves corresponding to different temperatures.
