Introduction
The word modulus (derived from Latin) broadly refers to the “measure” or “manner” of something. Different types of quantities are referred to as Moduli (plural of modulus) in Mathematics, Physics and Engineering . One category of moduli is called the Elastic Modulus.
What is an Elastic Modulus
An elastic modulus (also known as modulus of elasticity) is a general term which refers to an object’s resistance to being deformed elastically (as opposed to plastically, which implies permanent deformation) when a stress is applied to it. We know that stresses can be categorized in different ways and for this reason the corresponding elastic modulus can also be defined.
There are several types of Elastic Moduli:
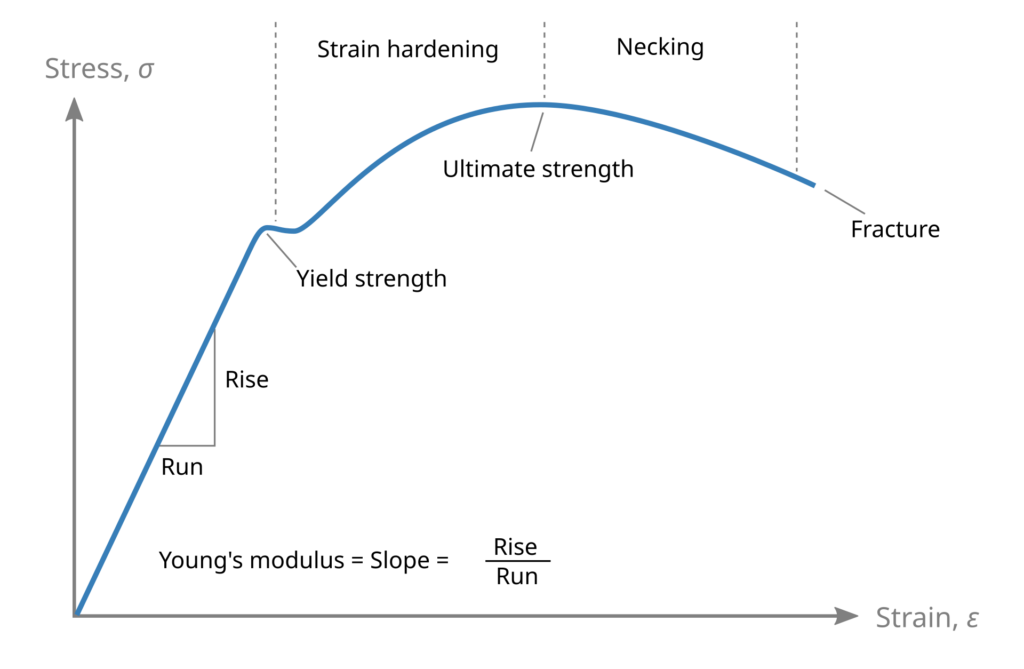
Young’s Modulus
Young’s modulus (E) describes tensile and compressive elasticity, or the tendency of an object to deform along an axis when opposing forces are applied along that axis; it is defined as the ratio of tensile stress to tensile strain. It is often referred to simply as the elastic modulus, tensile modulus, or compressive modulus.
Young’s modulus is the slope of the linear part of the stress–strain curve for a material under tension or compression.
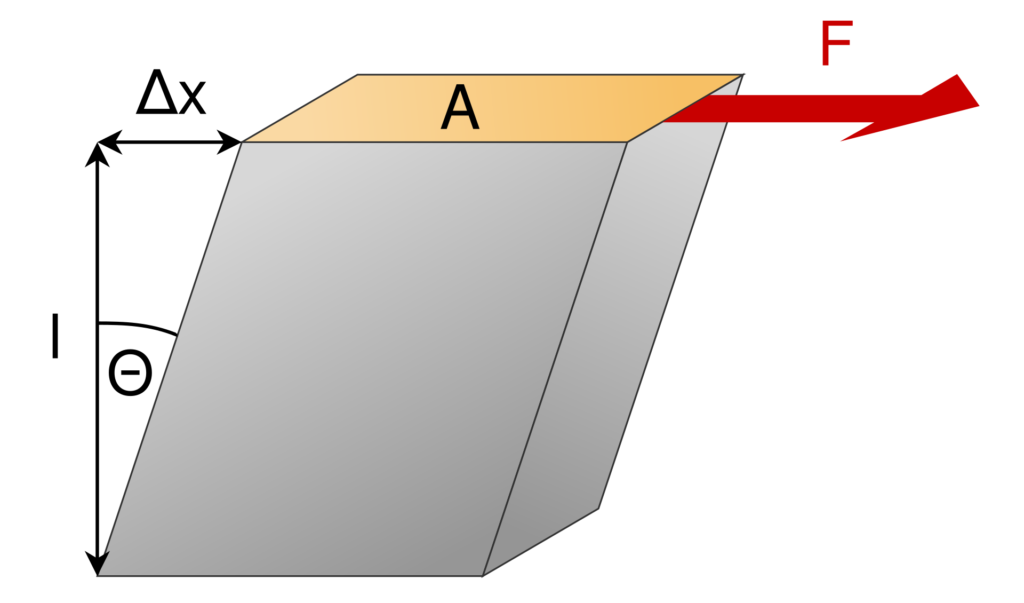
Shear Modulus
The shear modulus or modulus of rigidity (G ) describes an object’s tendency to shear (the deformation of shape at constant volume) when acted upon by opposing forces; it is defined as shear stress over shear strain. It can be calculated as the shear force per unit area divided by the displacement of the edge of that material. Shear deformation can be visualized in Figure 2.
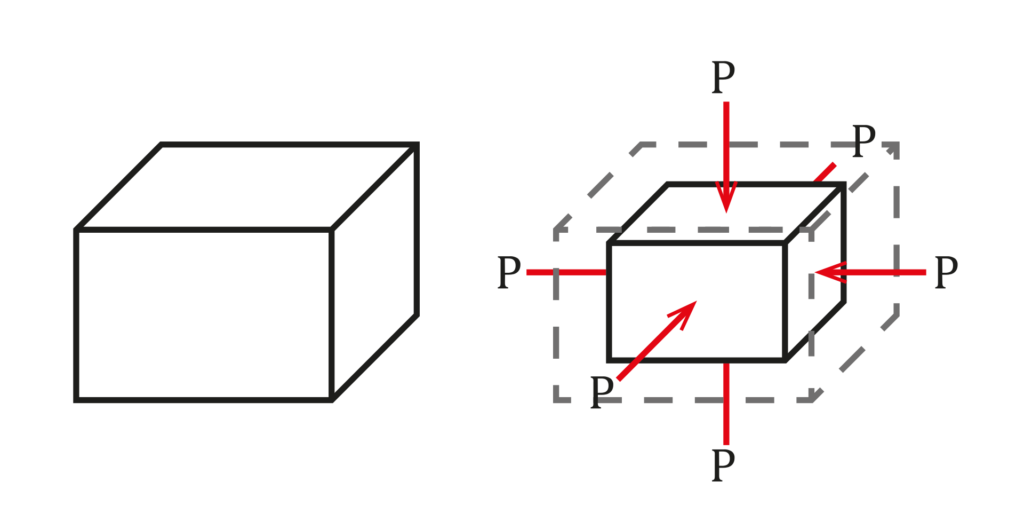
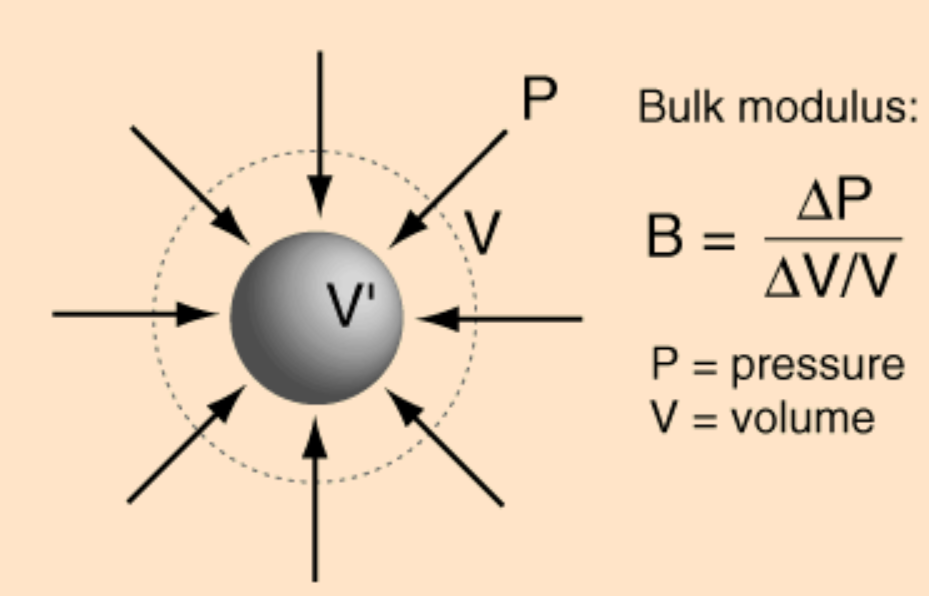
Bulk Modulus
The bulk modulus (K) describes volumetric elasticity, or the tendency of an object to deform in all directions when uniformly loaded in all directions; it is defined as volumetric stress over volumetric strain, and is the inverse of compressibility. The bulk modulus is an extension of Young’s modulus to three dimensions.
Flexural Modulus
Flexural modulus (Eflex) describes the object’s tendency to flex when acted upon by a moment. It is also referred to as bending modulus and is the material’s tendency to resist bending.
For very small strains in isotropic materials – like glass, metal or polymer – flexural or bending modulus of elasticity is equivalent to the tensile modulus or compressive modulus of elasticity.
However, in anisotropic materials, for example wood, these values may not be equivalent. Moreover, composite materials like fiber-reinforced polymers or biological tissues are inhomogeneous combinations of two or more materials, each with different material properties, therefore their tensile, compressive, and flexural moduli usually are not equivalent.
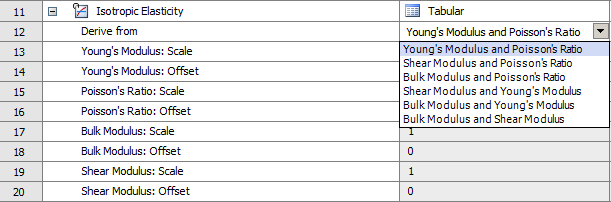
Assigning Material Modulus in Ansys Workbench
Ansys Mechanical allows the user to input Young’s Modulus, Shear Modulus and Bulk Modulus. Figure 5 shows how to access the option to input the modulus from engineering data in Ansys Workbench.