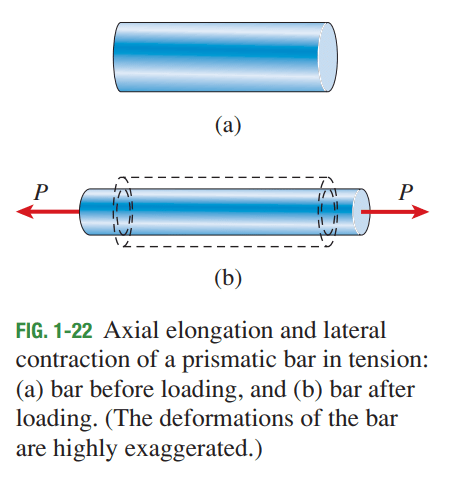
Axial stress is a normal stress and tends to change the length of a specimen. Axial stress may be tensile (positive) or compressive (negative). The image below shows a state of uniaxial stress, i.e., normal stress in only one direction. The axial stress associated with this is the Force P, divided by the cross sectional are of the bar:
Axial Stress = P/A
This page is part of The Encyclopedia of Stresses in Solids