A thin-walled pressure vessel is subjected to three mutually perpendicular stresses.
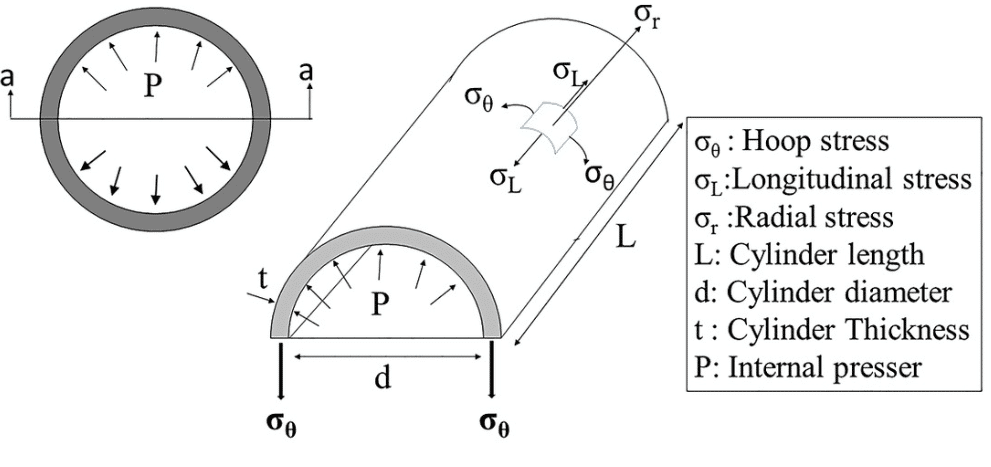
Hoop stress is the normal stress in the tangential direction. It is also called circumferential stress and acts along the circumference of a cylinder and resists bursting. Failure due to hoop stress will typically result in a pipe splitting in two halves. Hoop stress is a primary driver in pressure vessel design.
Longitudinal Stress acts along the axis of the cylinder, or the length of the pipe.
Radial Stress acts along the radial direction.
This page is part of The Encyclopedia of Stresses in Solids